Guide
Replicating a new DNA strand requires a stable and controllable nucleotide production unit. Now researchers at the University of Copenhagen in Denmark are showing how this process of human cells is regulated. They found that this regulation can be used to kill cancer cells.
Throughout life, human cells continue to divide and produce new cells. In this process, cells respond to metabolic fluctuations by regulating the rate of DNA replication as a guarantee of genomic stability. An article published in Science on November 10 illustrates how the replication fork dynamically responds to the cytological mechanisms of metabolic pathways. The researchers also showed that they can manipulate this rhythm and recommend it to kill cancer cells.
In human cells, the four nucleoside elements of DNA are produced by an enzyme called RNR. It has not been fully understood before that how the rate of production of RNR and the amount of nucleotides are consistent with the rate of DNA replication. Now, researchers at the University of Copenhagen have figured out the process of regulation: nucleoside production follows the same rhythm as DNA replication, and when the two are different, the cells regulate the process to make the two consistent.
The author of the article, Professor Jiri Lukas, said: "We can see that these processes follow the same periodic rhythm. We found that DNA replication slows down immediately before the nucleotide supply to the nucleotide factory RNR becomes extremely low. â€
Molecular mechanism of regulation
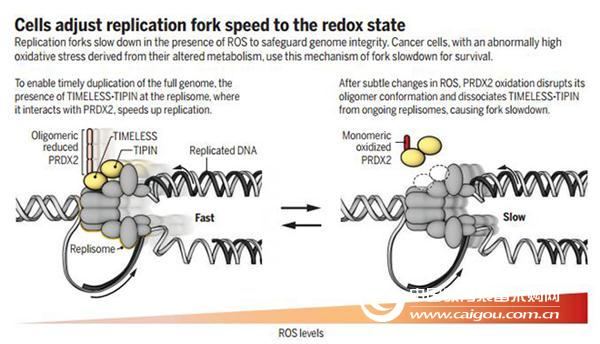
The team found that cells responded even when there was little change in the amount of nucleotides supplied. If nucleotide production does not go up, a chemical signal transmitted by reactive oxygen species (ROS) will slow DNA replication.
The study, published in Science, suggests that such communication between nucleotide supply and DNA replication rate may be due to the fact that all sites in the human genome that are actively replicating DNA contain a protein called PRDX2. Detect such chemical alarms.
When this happens, the PRDX2 protein releases a catalyst called TIMELESS in the DNA, which slows down the pace at which the cells replicate DNA. Slower DNA replication allows for the accumulation of nucleotide production back to the same rhythm as DNA synthesis. Because of this, there are almost always enough nucleotides to construct DNA, which is a very important point for making healthy genomes copy without errors.
Used to kill cancer cells
This discovery reveals the link between this mechanism and some diseases, especially cancer. Researchers have shown that they can stop the chemical signal that prompts cell nucleotide production problems. Under such conditions, the process of cell replication cannot be slowed down, and researchers believe that this will hinder the proliferation of cancer cells because they are particularly susceptible to high-speed replication.
Kumar Somyajit, the lead author of the study, said: "We found that cancer cells replicate their DNA very slowly because they have abnormal genomes, so DNA replication has many obstacles to overcome. When we slowly replicate the genome's ability After removal, cancer cells die because they cannot cope with many problems on DNA templates."
Shanghai Chuangsai Technology has excellent performance, interleukin cytokines, fetal bovine serum, electrophoresis equipment scientific instruments, raw material drug standards, chemical reagents, cell culture consumables, Shanghai Chuangsai, mass products special promotions, welcome to inquire!
Hand Dryer,jet hand dryer,bathroom hand dryer,hand dryer for toilet
TAISHAN YUEXIN INDUSTRIAL GROUP LIMITED , https://www.gdmetalplasticproducts.com