Square Circle Hui Book Scanner Matrix CCD Advantage: CCD technology was developed by Bell Labs in the United States in 1969. The earliest CCD designs were linearly arranged and the image quality was poor. In the 1980s, although CCD image sensors were flawed, high-resolution and high-quality CCDs were produced in the second half of the 1980s due to continuous research and difficulties. In the 1990s, a high-resolution CCD of megapixels was produced. At this time, the development of CCD has been advancing by leaps and bounds. It has been more than 20 years since the development of CCD.

In 2000, CCD technology developed rapidly. At the same time, the unit area of ​​CCD is getting smaller and smaller. Kodak made the world's first matrix CCD, but it is impossible to manufacture a large-area matrix CCD due to the complicated process. A high-definition image capture device manufactured by true color matrix CCD technology used in aviation for the first time in 2008. This is also a milestone in the development of CCD technology, and finally produced a true color giant true color matrix CCD. However, at that time, the giant true color matrix CCD manufacturing process was complicated and expensive, and was mainly applied in the aerospace and industrial fields.
Due to the low price of linear CCDs, the current highest resolution linear CCD collector is at 1000 yuan/bar, so most of the scanner brands on the market use traditional linear CCD technology. At present, scanner products using matrix CCD are mostly high-end non-contact book ancient book scanner products.
At present, the scanner market uses matrix CCDs, which are mainly divided into three types: small-area matrix CCD, RGB monochrome matrix CCD, and full-width true color matrix CCD.
1. Small-area matrix CCD: A frame needs to be scanned multiple times for software stitching. The error rate is high, and it is generally used in low-end book scanner products, such as the ps7000 and ps5000 series that Japan Konica failed to reach.
2, RGB monochrome matrix CCD: scanning color files need to be scanned multiple times to complete. Scanning speed is slow, generally used in low-end matrix book scanners, such as the French i2s book scanner.
3, full-width true color matrix CCD: full color point-to-point scanning technology, perfect image restoration. The scanning speed is fast, the color scanning takes only 0.3 seconds, and the full color processor is relatively expensive, and is generally applied to high-end non-contact scanning devices. For example, the German book2net book magazine volume scanner series.

With the commercialization of industrial-grade high-end CCDs, a space-grade full-frame true color matrix CCD is used to make scanners. This new design greatly increases the scanner's scanning speed (A2 400dpi color 0.3 seconds), which is three times faster than traditional linear ccd book scanners and RGB monochrome matrix scanners. The true color matrix book scanner is a one-time point-to-point scan imaging that makes the overall restoration of the scanned image better and achieves zero distortion of the image. Moreover, the true color matrix scanning one-time point-to-point scanning method does not need to move the progressive (multiple) scanning like the linear or RGB monochrome matrix scanner, which reduces the transmission mechanism and greatly increases the durability of the book scanner. It also reduces the light pollution of linear scanning equipment and reduces the damage of precious materials in the digitization process. The life of the matrix CCD is more than 300 million pages, which is more suitable for a large number of ancient books.
Traditional linear CCD scanner
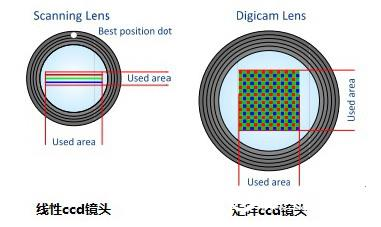
The traditional scanner makes the white light scan the document line by line, uses the linear CCD sensor to capture the three colors of RGB, the image passes through the lens, and then presents to the linear CCD sensor. The light source and the linear CCD move synchronously, and the image is reflected by the lens into the CCD, and finally Complete digital imaging. In book scanners, linear CCD, lens system, and rotating mirror scanning methods are often used to simulate the movement of an object to acquire scan results. During the scanning process, the linear CCD sensor captures the information in the original in the order of red, green, and blue lines. When the CCD processor converts these lines into the correct order, the line-by-line stitching completes the overall image. Although the production process of linear scanners is relatively mature, the linear ccd scanning equipment needs to move back and forth between the ccd and the light source during the scanning process, which has high lubrication requirements for the transmission system, and fluctuations in the movement will occur. Image distortion and water ripple appear. Especially in the archaeological work of the old archives, the environmental dust is large, which has a great influence on the lubrication of the ccd track. Progressive light can also cause some damage to the surface of precious media and the eyes of the processing personnel. Moreover, most scanner manufacturers choose a small-sized linear CCD (A4 format) because of the production cost. In the design of a larger than A4 format scanning device, multiple CCD groups are used for splicing. This has the advantage of using the lowest The cost of producing larger format and higher resolution scanning equipment, but the phenomenon of splicing errors is difficult to avoid.
Space-grade matrix CCD sensor assembly
The space-grade matrix CCD sensor assembly uses a planar CCD consisting of very small pixels. His collection method is a point-to-point true color one-time acquisition.
The aerospace-grade true color matrix CCD sensor can convert a single pixel optical signal on the surface of the original into an electrical signal, and the acquisition speed is instantaneously completed. It is usually only 0.3 seconds to scan the A2 full color image at 600 dpi with high precision. Because image acquisition is done in one shot at a time, image acquisition color reproduction is better, especially in the collection of special color media (such as gold, silver), these color linear ccd can not be collected. And the true color matrix ccd can perform stereoscopic acquisition on the real object. The color filter provides a very high color saturation for the three consecutive rows of red, green and blue CCD elements, and the image is collected as a whole. A high-quality true color matrix CCD has a relatively large pixel size, and a 10 μm × 10 μm size is a typical pixel size value. Larger pixel sizes can help reduce noise and other effects that may affect image quality.
The chart below shows how a matrix CCD sensor is generated.
Collecting gold book effects

Rechargeable Sonic Electric Toothbrush
Rechargeable Sonic Electric Toothbrush,Adult Electric Toothbrush,Portable Household Electric Toothbrush,Special Sonic Electric Toothbrush
ZHEJIANG SHENGFA ELECTRIC APPLIAMNCES CO.,LTD , https://www.sfelectricappliances.com