Researchers at the University of Oxford have discovered a new way to print living tissue from cells grown in the laboratory. This living tissue can be used as a human tissue model to eliminate the need for animal experiments.
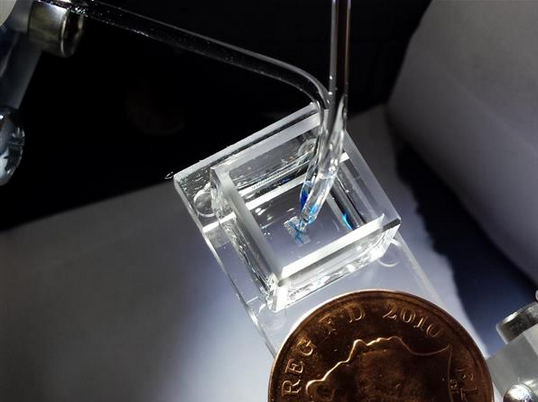
3D printing of living tissue is one of the most exciting applications in modern science. For a few patients with complex diseases, 3D printing researchers, and members of animal protection organizations, the benefits of this research are self-evident. of.
Once the 3D printing bio-tissue technology is perfected, it will serve as a means of repairing damaged areas of the human body, which is its main application. It can also be used to test experimental drugs and medical procedures, and through living tissue, researchers can observe the reaction of certain drugs with human tissues.
This is a good thing for people in animal protection organizations. The emergence of these living tissues can reduce the need for laboratory experiments in animals, and the results of research using living tissue are more reliable than those conducted from animals because Living tissue is closer to human tissue.
A research paper was published in Science Report: An interdisciplinary team at Oxford University has demonstrated a new way to print 3D human and animal tissue structures.
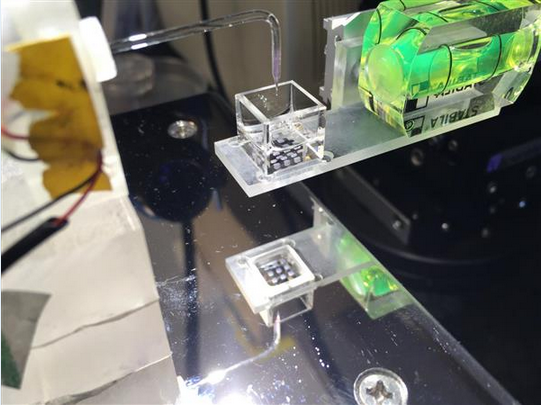
Led by Hagan Bayley, a professor of chemistry at Oxford University, the team discovered a way to create a living tissue structure in an independent cell and remain intact.
This "droplet-based 3D printing technology " involves 3D printed cells wrapped in a layer of lipid coating that protects the droplets of the nanoparticles, which is said to improve the survival of individual cells.
Dr. Alexander Graham said: "Our goal is to create 3D living tissue that shows the basic behavior and physiology of natural organisms. We have to design a high-resolution cell printing platform that replicates, including stem cells, through relatively inexpensive components. a series of complex artificial tissues."
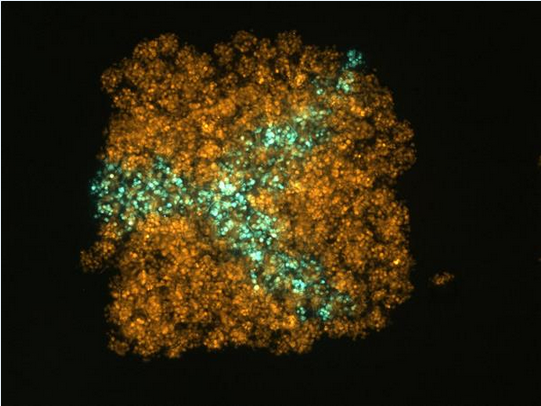
The research team hopes that the research will have a positive impact on health care around the world, and will invest in the production of renewable human tissue models to eliminate the need for animal experiments and new tissue regeneration therapies.
Given the potential impact of 3D printing technology, researchers have begun to focus on the commercialization of this technology. In January 2016, OxSyBio, a London-based medical 3D printing company, emerged from Bayley Labs, which aims to commercialize new technologies in "industrial and biomedical".
New complementary printing technologies will be tested in the coming months, and researchers will be able to experiment with a wider range of living hybrid materials.
Dr. SamOlof, CTO of OxSyBio, said: "We have many potential bioprinting applications that we believe will be able to create personalized treatments by using cells from patients to simulate or enhance natural tissue function. In the future, 3D Printing live tissue may also be used for diagnostic applications, such as drug or toxin screening."
Dr. Adam Perriman of the School of Cellular and Molecular Medicine at the University of Bristol added: “The 3D printing of adult stem cells and their ability to differentiate, demonstrates the enormous impact this new approach has on regenerative medicine worldwide.â€
(Compiled from 3ders.org)
Q-BOX Double walled drawer box system
Q-Box Double Walled Drawer Box System,Double Walled Drawer Box System,Kitchen Drawer System,Under Mount Slide Cabinet
Foshan city boucheron precision hardware co.,ltd , https://www.chinadrawerbox.com