Compared with solvent inks, high-grade flexographic inks have a great influence on the drying speed of inks on high-speed printing presses due to the high evaporation heat of water. In order to solve the problem of drying, printing companies generally adopt higher temperature, lower humidity and higher wind speed and air volume to promote the evaporation of water, but they will inevitably increase additional investment. Ink manufacturers should solve this problem from the formulation point of view, that is, water-based inks. The high solids differentiation of the formulation reduces the amount of ink transferred to the substrate being printed (this can be achieved by reducing the plate depth).
For printing companies, this is an effective way to reduce ink consumption, save energy, and reduce costs. There are two cases to increase the solid content. The first is to increase the resin content, but in order to obtain a good coloring power, the thickness of the ink film must be increased, which is not conducive to drying; the second is to increase the pigment content, while reducing the thickness of the ink film Better coloring power is guaranteed. However, high pigment content is bound to result in high viscosity. In order to facilitate high-speed printing, a high-solid, low-viscosity ink formulation system must be used. This article mainly discusses the influence of additives (including co-solvents) on the ink viscosity, and provides a theoretical basis for obtaining the ideal application viscosity of jadeite.
First, the experimental part
1. Main raw materials
Acrylic resin, Tg=98° C., acid value=205 mgKOH/g, MW=6500, used as a dispersion resin; high-pigment carbon black; polyacrylate used as a defoamer; A1, polyoxyethylene octylphenol ether sulfate Sodium salt, used as dispersant; A2, acetylene glycols, used as dispersant; A3, EO/PO block copolymer, used as dispersant; A4, polyoxyethylene fatty alcohol condensate, used as dispersant .
2. Basic formula 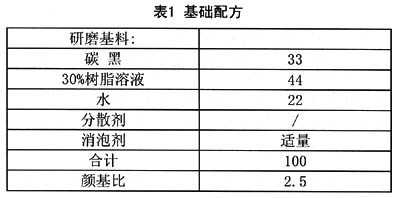
3. experimental device
In this experiment, a medium mill (sand mill) small-scale test equipment was used to achieve dispersion by applying forces to the pigment by the medium beads and centrifugal force generated by high-speed rotation of the disk impeller. Glass beads are used as grinding media in the media mill, and the volume is 100% of the volume of the dispersed material, as shown in Figure 1: 
4. Ink performance characterization method
(1) tinting strength Tinting Strength reference GB/T 13217.6-91 detection
(2) gloss Gloss reference GB/T 13217.6-91 detection
(3) Fineness Firless Tested according to GB/T 13217.3-91
(4)ViscoSity Viscosity according to GB/T 13217.4
(5) cup method: #2 Chaun Cup Tu #4 cup;; rotational viscometer method: using Brookfield RVT type viscometer
(6) Surface tension Sensadyne 6000 surface tension meter, ink/water = 1/1, 25°C
Second, results and discussions
1. Effect of dispersants
In order to investigate the mechanism of the dispersant's influence on the viscosity of the ink system, and also to take into account the influence of the dispersant on the dispersion effect, we first selected several wetting and dispersing agents for the experiment. First, the HLB value was determined by the water dispersion method (hydrophilic and lipophilic). The equilibrium value), that is, a small amount of surfactant was mixed with water, the properties of the final dispersion were observed and the HLB value of a certain surfactant was roughly evaluated. The results are shown in Table 2. Among them, insoluble or non-dispersive is 1-4, unstable or poorly dispersed is 5-6, after strong oscillating, milky dispersion is 7-8, stable milky dispersion is 9-10, translucent or gray dispersion For 11 to 13, the clear solution is >13.

The effect of different wetting and dispersing agents on the viscosity and the dispersing effect was investigated in accordance with the predetermined basic recipe and the predetermined grinding procedure.

From the results in Table 3, it can be seen that A1, A2, A3, and A4 can significantly reduce the dynamic surface tension of ink, with the formulas A1 and A2 (respectively, sodium polyoxyethylene octylphenol ether sulfate). Acetylene glycol is the most significant, and the lower surface tension is also more pronounced for viscosity reduction. In fact, when the ink formulation is designed, the dispersant causes a large drop in the viscosity to be a very practical function of the dispersing agent. We also see that A3 and A4 have obvious stabilizing foam effect (possibly because the polymer structures of A3 and A4 are not easy to move), which will inevitably increase the amount of defoamer, and the increase in defoamer dosage may lead to fish Eyes, shrinkage holes and other defects increase. In addition, the water resistance of A1 and A4 may be reduced due to their strong hydrophilicity, which will also affect their drying performance. High dynamic surface tension and stable foaming tendency all significantly affect the dispersion effect. The added wetting and dispersing agent should also consider the influence on the film forming performance of the ink while reducing the viscosity and improving the dispersion performance. The above experimental results show that only when A2 is used in an amount of 0.5 wt%, the surface tension and viscosity are significantly reduced, and at the same time, an ideal dispersion performance and a good film forming performance are obtained. Of course, adjusting the amount of auxiliary agent for further experiments may improve the performance of the auxiliary agent. (to be continued)
DELIN HAIR COSMETICS , https://www.hairdyecolorfactory.com